Products
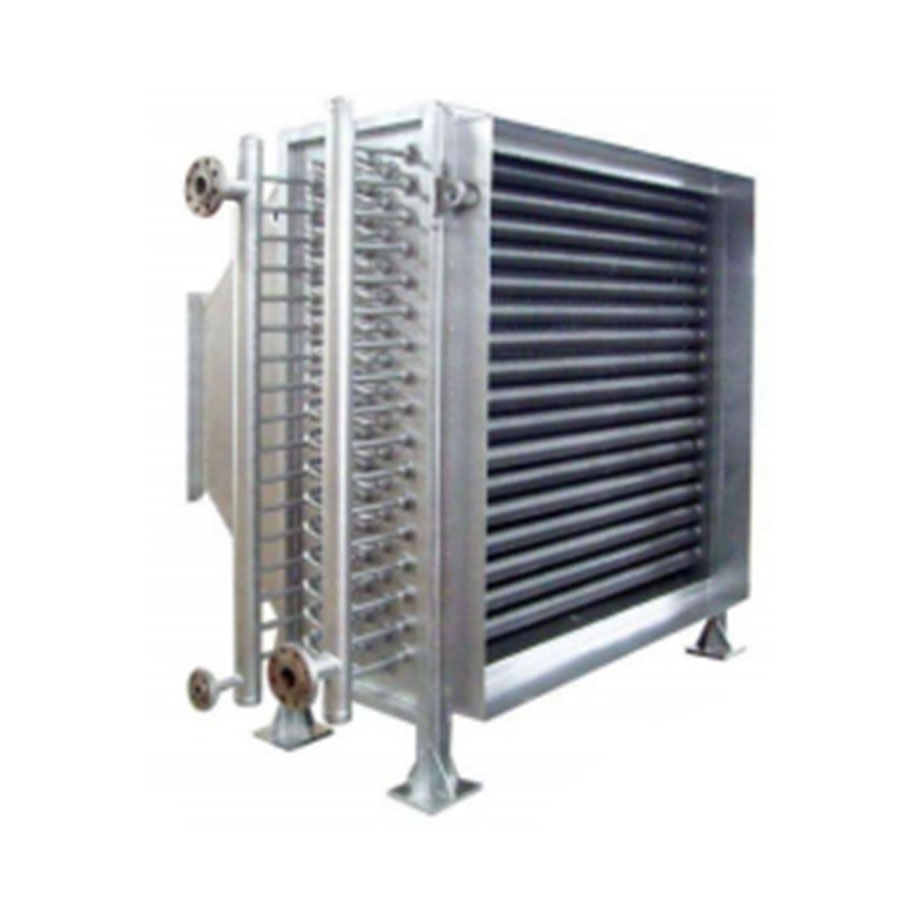
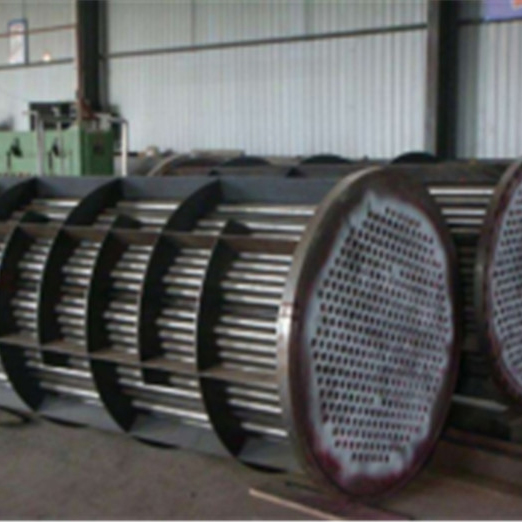
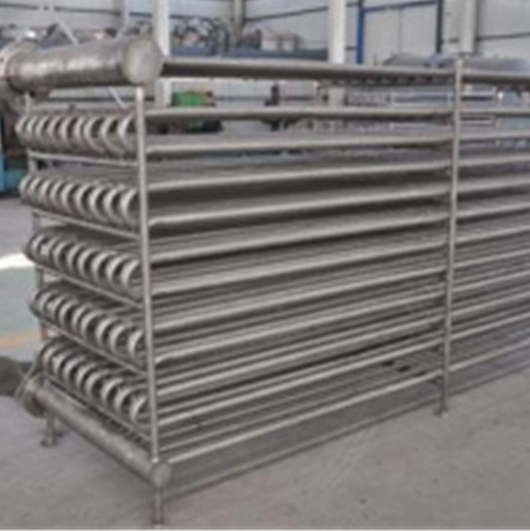
Heat Exchanger (Condenser For Vapor And Water)
Heat exchanger
Standard
JIS G3461
JIS G3462
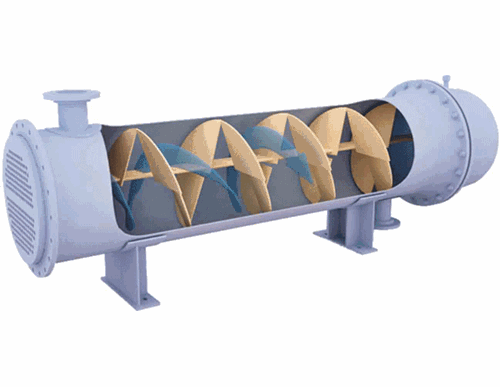
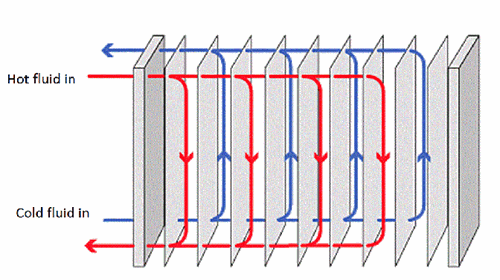
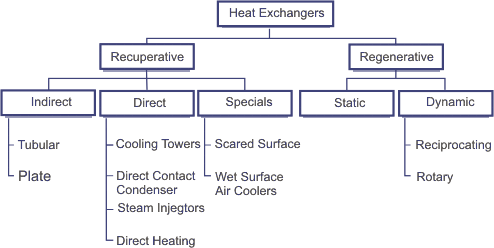
Application
It is used for boiler and heat exchanger inside & outside tube
Main Steel Tube Grades
STB340, STB410, STB510, STBA12, STBA13, STBA20, STBA22, STBA24,
Heat exchangers are used to transfer heat from one medium to another. These media may be a gas, liquid, or a combination of both. The media may be separated by a solid wall to prevent mixing or may be in direct contact. Heat exchangers can improve a system’s energy efficiency by transferring heat from systems where it is not needed to other systems where it can be usefully used.
For example, waste heat in the exhaust of an electricity-generating gas turbine can be transferred via a heat exchanger to boil water to drive a steam turbine to generate more electricity (this is the basis for Combined Cycle Gas Turbine technology).
Another common use of heat exchangers is to pre-heat a cold fluid entering a heated process system using heat from hot fluid exiting the system. This reduces the energy input necessary to heat the incoming fluid to working temperature.
Specific applications for heat exchangers include:
Heating a cooler fluid using the heat from a hotter fluid
Cooling a hot fluid by transferring its heat to a cooler fluid
Boiling a liquid using the heat from a hotter fluid
Boiling a liquid while condensing a hotter gaseous fluid
Condensing a gaseous fluid by means of a cooler fluid
The fluids within heat exchangers typically flow rapidly, to facilitate the transfer of heat through forced convection. This rapid flow results in pressure losses in the fluids. The efficiency of heat exchangers refers to how well they transfer heat relative to the pressure loss they incur. Modern heat exchanger technology minimizes pressure losses while maximizing heat transfer and meeting other design goals like withstanding high fluid pressures, resisting fouling and corrosion, and allowing cleaning and repairs.
To utilize heat exchangers efficiently in a multi-process facility, heat flows should be considered at a systems level, for example via ‘pinch analysis’ [Insert link to Pinch Analysis page]. Special software exists to facilitate this type of analysis, and to identify and avoid situations likely to exacerbate heat exchanger fouling





